Turbo vs naturally aspirated engine introduces a fascinating debate in the automotive world, where engineers and enthusiasts alike weigh the benefits of forced induction against the simplicity of naturally aspirated designs. Turbocharged engines utilize a turbine to enhance air intake, resulting in heightened power and efficiency, while naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure, offering a more direct and immediate throttle response. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge of engine technology.
Discover more by delving into Top performance cars 2024 further.
This exploration of turbocharged versus naturally aspirated engines will cover their fundamental principles, performance metrics, fuel efficiency, maintenance needs, and the unique driving experiences they provide. By examining popular vehicle examples and engaging with the latest trends, readers will gain insights into which engine type best suits their preferences and driving styles.
Find out further about the benefits of 2024 turbocharged sports cars that can provide significant benefits.
Turbo vs Naturally Aspirated Engines: A Comprehensive Analysis
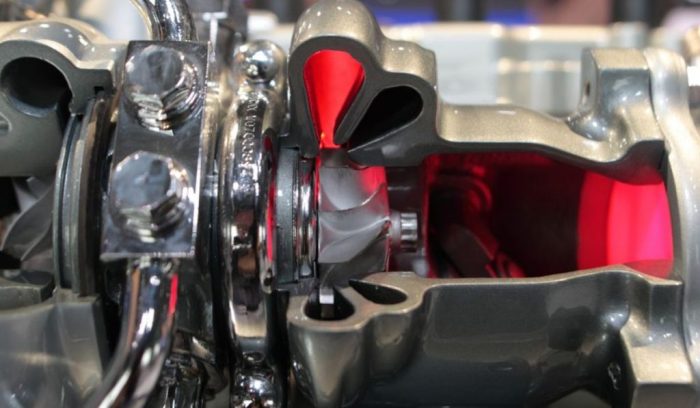
The automotive world is often split between two primary types of internal combustion engines: turbocharged and naturally aspirated. Each type possesses distinct characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks that cater to different driving preferences and performance requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for consumers and enthusiasts alike, as it influences vehicle choice, driving experience, and overall satisfaction on the road.
Definition and Overview
Turbocharged engines utilize a turbine-driven forced induction system that compresses air entering the engine. This process allows for more air and fuel to be mixed, resulting in increased power output without significantly increasing engine size. Conversely, naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber, which limits their maximum power output compared to turbocharged counterparts. Vehicles such as the Ford Mustang GT often feature naturally aspirated engines, while models like the Subaru WRX are commonly equipped with turbocharged engines.
Performance Comparisons
When comparing the power output and torque characteristics of turbocharged versus naturally aspirated engines, turbocharged engines typically excel. They can produce higher horsepower figures due to the additional air supplied by the turbocharger. The following highlights the performance differences:
- Turbocharged engines often deliver higher torque at lower RPMs, providing better acceleration from a standstill.
- Turbocharging significantly impacts acceleration, often allowing vehicles to reach higher speeds in shorter time frames.
- Naturally aspirated engines are known for their immediate throttle response, making them ideal for spirited driving.
Fuel Efficiency
Turbocharged engines can offer improved fuel efficiency, particularly during highway driving conditions where they can operate at a more optimal air-fuel mixture. Studies show that turbocharged engines can achieve up to 20-30% better fuel economy compared to naturally aspirated engines under certain conditions. To support this, statistics indicate that a turbocharged 2.0-liter engine can provide comparable power to a larger naturally aspirated engine while consuming less fuel. To maximize fuel efficiency for both engine types, owners can adopt practices such as regular maintenance, avoiding aggressive driving, and utilizing higher-quality fuels.
Maintenance and Reliability

Maintenance requirements differ significantly between turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines. Turbocharged engines often necessitate more frequent oil changes and may require additional cooling systems to manage heat generated by the turbo. Common reliability issues for turbocharged engines include turbo lag and compressor failure. In contrast, naturally aspirated engines tend to be more straightforward in design, leading to potentially lower maintenance costs and higher reliability. Owners can extend the lifespan of both engine types by adhering to manufacturer maintenance schedules and ensuring proper care.
Driving Experience, Turbo vs naturally aspirated engine
The driving experience between turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines varies widely. Turbocharged engines typically offer a unique power delivery that can feel exhilarating, especially under acceleration. However, some drivers may notice a slight delay in response, known as turbo lag. In contrast, naturally aspirated engines provide a more linear power band, giving drivers a direct connection between throttle input and engine response. Each engine type performs differently in various driving conditions:
- City driving favors naturally aspirated engines due to their immediate throttle response.
- Highway driving often benefits from turbocharged engines, which maintain power at higher speeds.
- Off-road scenarios may see preference for naturally aspirated engines due to their consistent power delivery.
Environmental Impact
The emissions profile of turbocharged engines often shows lower carbon dioxide output compared to naturally aspirated engines due to their improved fuel efficiency. However, the production of particulate matter can be higher in some turbocharged models. Both engine types contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, but advancements in technology, such as better catalytic converters and exhaust systems, continue to reduce their environmental footprints. Various regions are enacting stricter regulations concerning emissions, pushing manufacturers to innovate and enhance engine efficiency.
Future Trends
Emerging technologies are redefining both turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines. Innovations such as variable geometry turbochargers and twin-scroll designs enhance performance while maintaining efficiency. The rise of electric and hybrid technologies is shaping the future of engine design, as manufacturers increasingly focus on combining traditional engine methods with electric power sources. Consumer preferences are predicted to shift towards more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly options, highlighting a potential increase in hybrid vehicles that leverage the strengths of both types of engines.
End of Discussion
In summary, the discussion surrounding Turbo vs naturally aspirated engine reveals that both types of engines offer unique advantages and drawbacks, shaping the way we experience driving. While turbocharged engines excel in power and fuel efficiency, naturally aspirated engines stand out for their responsiveness and simplicity. As automotive technology continues to evolve, understanding these differences will empower consumers to make informed decisions about their vehicle choices, ensuring a driving experience that aligns with their individual needs.